Transdisciplinary research aims to address complex societal issues by integrating knowledge from different disciplines and involving stakeholders from outside academia. This approach can lead to transformative societal impacts
According to Merritt Polk
Linked to the ENHANCE glossary, the Alliance sees societal impact as part of the broader social character of transdisciplinarity. In this context, societal impact is an element of the logical structure (Fig.1), which includes terms such as social participation, relevance, effect, impact and responsibility. Societal impact is just one of at least five different forms of social contribution and interdependencies with transdisciplinarity. Importantly, these internal connections are multidimensional and mutual between all five characteristics, and each is necessary to make transdisciplinarity effective and socially relevant.
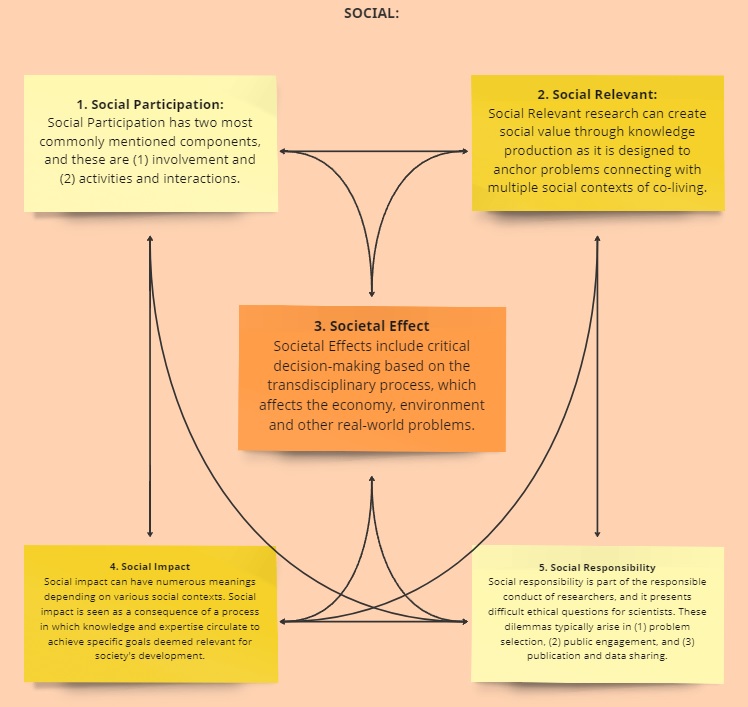
For the ENHANCE Alliance as a result of mapping the transdisciplinary initiatives, societal impact is defined as added value and comprises a wide range of linkages to address and solve societal problems. Depending on the focus of the identified transdisciplinary initiative and the strategic orientation of the university, societal impact as added value can be achieved or enhanced in the following ways:
Transdisciplinary Process Design: Initiating a collaborative process that begins with co-framing a societal problem, co-producing new knowledge, and reiterating/reflecting on the transferability for potential upscaling in the scientific and societal spheres. By fostering strong synergies among the various stakeholders, they become more engaged in the problem-solving journey, leading to increased receptivity to the research outcomes of the transdisciplinary initiative.
Facilitating Knowledge Exchange and Integration: Enabling knowledge exchange and knowledge integration for transdisciplinary research processes and projects in a long-term perspective. This approach supports sustainable growth and development over time.
Addressing Societal Challenges: Through advanced research areas and programs as well as collaborative design of research concepts, prototypes, pilot projects and strategic partnerships (e.g. with industries and companies), solutions are co-created to address societal challenges.
Raising Societal Awareness: Emphasising the necessity of co-designed solutions that integrate research and business teams with other stakeholders, raising awareness within society about the importance of collaborative approaches.
The transdisciplinary initiatives mapped at ENHANCE universities vary considerably in their focus on societal impact in terms of innovative and creative strategies. This variation depends on funding, strategic approach, methods and formats – and, most importantly, the levels of engagement. A broad common understanding of transdisciplinarity is fundamental to anchor this research principle for achieving the societal impacts and as a framework in the ENHANCE universities and to encourage further initiatives of knowledge exchange and collaboration between science and society for sustainable development. Together with the diverse approaches of the transdisciplinary initiatives within the ENHANCE alliance, it is the foundation for creating synergies between different stakeholders to promote the production and dissemination of new integrated knowledge and fostering sustainable solutions for societal transformation.
ENHANCE materials
Discussion, comparison and analysis of transdisciplinary approaches in ENHANCE partner universities by Kathrin Wieck
Catalogue of joint advisory for supporting transdisciplinary research by Sarah Fowkes and Kathrin Wieck

